Track mileage automatically
Get startedHow to calculate mileage reimbursement in Canada
The formula for figuring out your reimbursement for business mileage in a car is as simple as:
[km] * [reimbursement rate].
The 2026 mileage reimbursement rate in Canada is:
- 73 cents per kilometre for the first 5000 km
- 67 cents per kilometre after that
- An additional 4 cents per kilometre in the Northwestern Territories, Nunavut and Yukon
Note that the CRA sets a lower mileage reimbursement rate for every business kilometre after the first 5.000, slightly complicating the formula:
[5000 km] * [rate 1] + [Additional km] * [rate 2]
If you are an employee, your company may use a rate different to the one CRA sets. Additionally, your employer might also have different policies. Learn what to look for in our guide for employees.
Mileage reimbursement calculator
Quick guide to our simple calculator:
- Choose between CRA's rates for this or the previous year or set one yourself
- Then give the distance in kilometres you drove or expect to drive for work
- Check whether you're from the Northwest Territories, Yukon, and Nunavut
- The calculator will compute your reimbursement in CAD
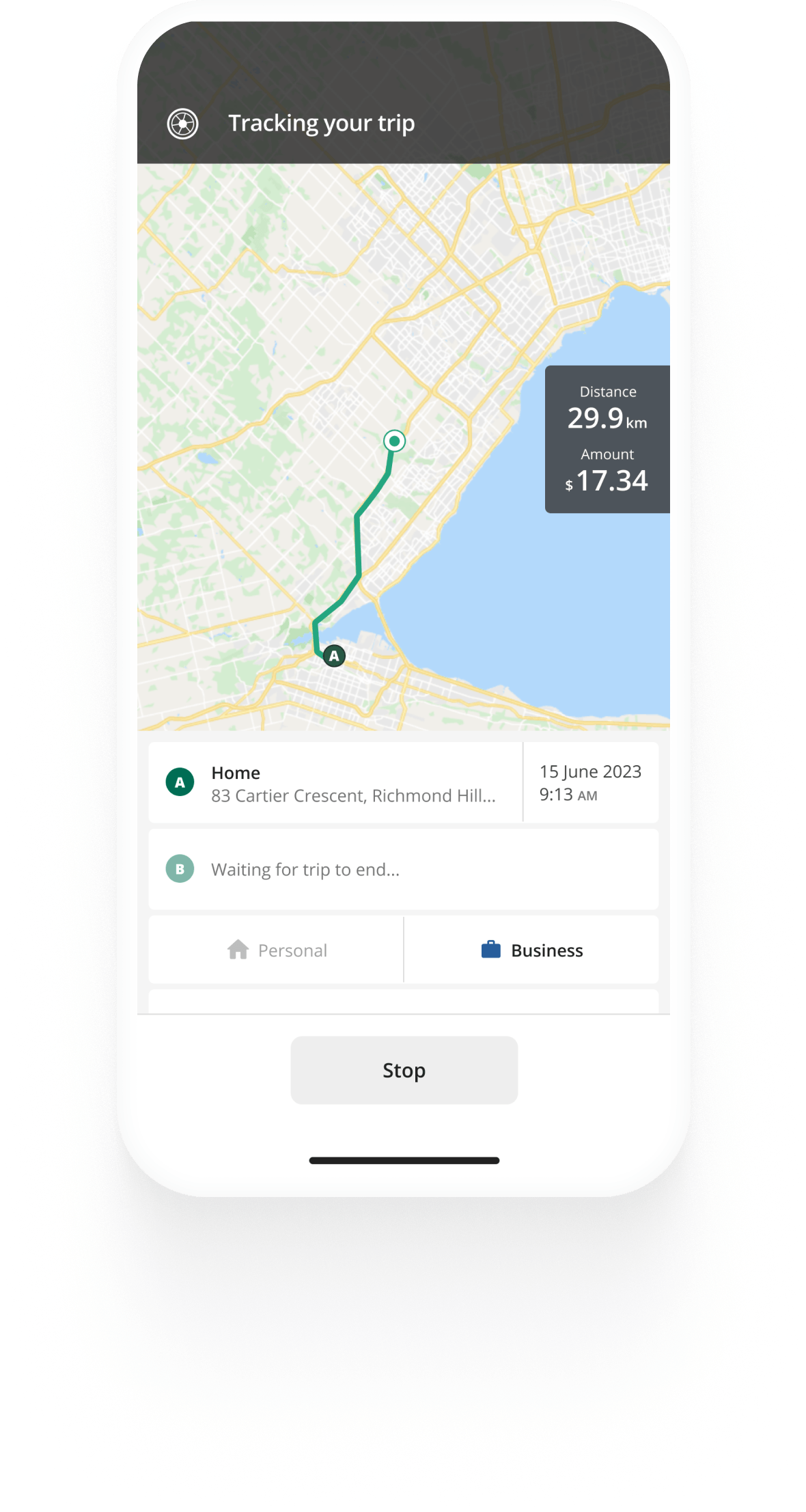

Track business driving with ease
Trusted by millions of drivers
Automate your logbook Automate your logbook
Automatic mileage tracking and CRA-compliant reporting.
Get started for free Get started for freeCalculate mileage reimbursement in Excel
If you need a mileage log and prefer working out your mileage in a spreadsheet, we have prepared a free template: Free mileage log template.
Calculate mileage deductions from the CRA
You can deduct reasonable motor vehicle expenses when you have receipts to support them. These can include licence & registration fees, fuel and oil costs, or electricity costs for zero-emission vehicles, as well as your insurance costs, interest on a car loan, maintenance, repairs, and/or leasing costs. To calculate your mileage reimbursement using a logbook, first, you will need to decide which logbook method to use:
- The full logbook method
- The simplified logbook method
The full logbook method
Using the full logbook method, you must record every kilometre driven with a breakdown of what is personal and what’s business-related driving.
For any trip logged as business-related, you’ll need to note the following:
- Date
- Destination
- Purpose
- Number of kilometres driven
In addition, you’ll need to record your vehicle’s odometer readings at the start and end of the year (or fiscal period). Alternatively, if you change vehicles during the year, you’ll need to record the dates that you changed vehicles as well as the odometer readings when the change was made.
Motor vehicle expenses can only be deducted if they are reasonable and if you have receipts to back them up, according to the CRA. Deductible expenses include:
- Licence & registration costs
- Fuel & oil
- Electricity (for zero-emission vehicles)
- Insurance
- Maintenance & repairs
- Leasing costs
- Interest on money borrowed to buy the motor vehicle
Finally - if you use more than one vehicle for business purposes, remember to record the kilometres for both vehicles separately, as well as record your expenses for each vehicle. You must calculate your deduction for each vehicle separately.
Now, let’s look at an example of calculating your mileage reimbursement from the CRA through the full logbook method.
Example: During the year, you have recorded a total of 12,000 km - 8,000 km of which have been business-related - and you have incurred car-related expenses of $4,000. To calculate your deduction, you need to multiply your expenses by your business use percentage:
( [business km] / [total km] ) * [expenses], or:
( [8,000 km] / [12,000 km] ) * $4,000 = 0.75 * $4,000, for a total deduction of $3,000.
The simplified logbook method
Once you have a full 12 months of driving (both business and personal) recorded in a logbook, you can use that to establish a “base year” for your business usage.
When the base year is established, you can then use a three-month sample from the current year to forecast your business usage for the entire year.
There are some limitations here - the calculated business use for the sample period must be within 10% of the business use in the base year.
If business usage in the sample period is different from the base year by more than 10%, the sample period logbook will only be reliable for the 3 months of driving you recorded, and you will need to determine business usage for the remainder of the year by logging all of your driving once more.
The formula that the CRA requires to calculate your annual business use using the simplified logbook method is:
(Sample year period % ÷ Base year period %) × Base year annual % = Calculated annual business use
Example 1:
Jenny has completed a logbook for all of 2023, which showed her business use percentage in each quarter as 48% / 53% / 61% / 35%, with the average annual business use of 49%. From January to March of 2024, she maintained a sample logbook showing that her business use was 57%. For the same period of the base year, her business use was 48%. The calculated annual business use is worked out as follows:
(Sample year period % ÷ Base year period %) × Base year annual % = Calculated annual business use
(57 % ÷ 48 %) × 49 % = 58%
In this instance, her sample logbook would be accepted for the year, with the annual business use of 58% - as this is within 10% of the base year’s business use of 49%.
Example 2:
Steve has completed a logbook for 2022 which showed his business use percentage in each quarter as 34% / 35% / 36% / 35%, with an average annual business use of 35%. In 2023, his usage was consistent with 2022 percentages; however, from January to March of 2024, his business travel increased, and the business usage percentage increased to 60%. When comparing this to the January - March period of 2022, where the business use of his car was 34%, the calculated annual business use is worked out as follows:
(Sample year period % ÷ Base year period %) × Base year annual % = Calculated annual business use
(60 % ÷ 34 %) × 35 % = 62%
As you can see above, Steve’s calculated business use is more than 10% above the annual business use in his base year. Therefore, his base year record will no longer be suitable, and he should consider establishing a new base year by maintaining his logbook for a new 12-month period.
Work out the mileage reimbursement you can claim
To calculate your reimbursement using either logbook method, you must know the business use percentage of your total kilometres. Let’s look at a simple example:
At the end of the financial year, your logbook shows a record of 35,000 total kilometres. Of the 35,000 kilometres, 80% were for business purposes.
After adding up all of your expenses for the year from the receipts and invoices you’ve kept, your total car-related expenses are $10,000 for the financial year. Calculate your mileage reimbursement by following this calculation:
[Car expenses] x [Business Use %] = [Deduction]
$10,000 x 80% = $8,000
You can claim your mileage reimbursement for more than one car. You will need to keep a separate logbook for each vehicle, plus separate receipts and invoices for each of them.
Tired of logging mileage by hand?
Effortless. CRA-compliant. Liberating.
CRA Mileage Guide
- For Self-Employed
- For Employees
- For Employers
- Mileage Log Requirements
- How To Calculate Mileage Reimbursement
- Is Car Allowance Taxable?
- Claim Motor Vehicle Expenses In 5 Steps
- Current and Historic CRA Mileage Rates
- Historic Mileage Allowance Rates
- Current CRA Mileage Rates